
Description
iLund4u is a bioinformatics tool designed for the search and
annotation
of accessory genes and hotspots across large proteome datasets. This web application
focuses
on iLund4u's protein annotation mode, enabling users to determine whether homologues
of a
query protein are encoded within variable islands and hotspots.
It can help in protein function prediction by applying principles such as guilt by
association, and co-localisation.
Source code available at the GitHub Page.
We also recommend visiting the tool's
detailed documentation website that provides an algorithm description,
example-driven
guide, and documentation to the command-line version and python API.
See our preprint:
Egorov et al. bioRxiv, 2024
iLund4u pipeline
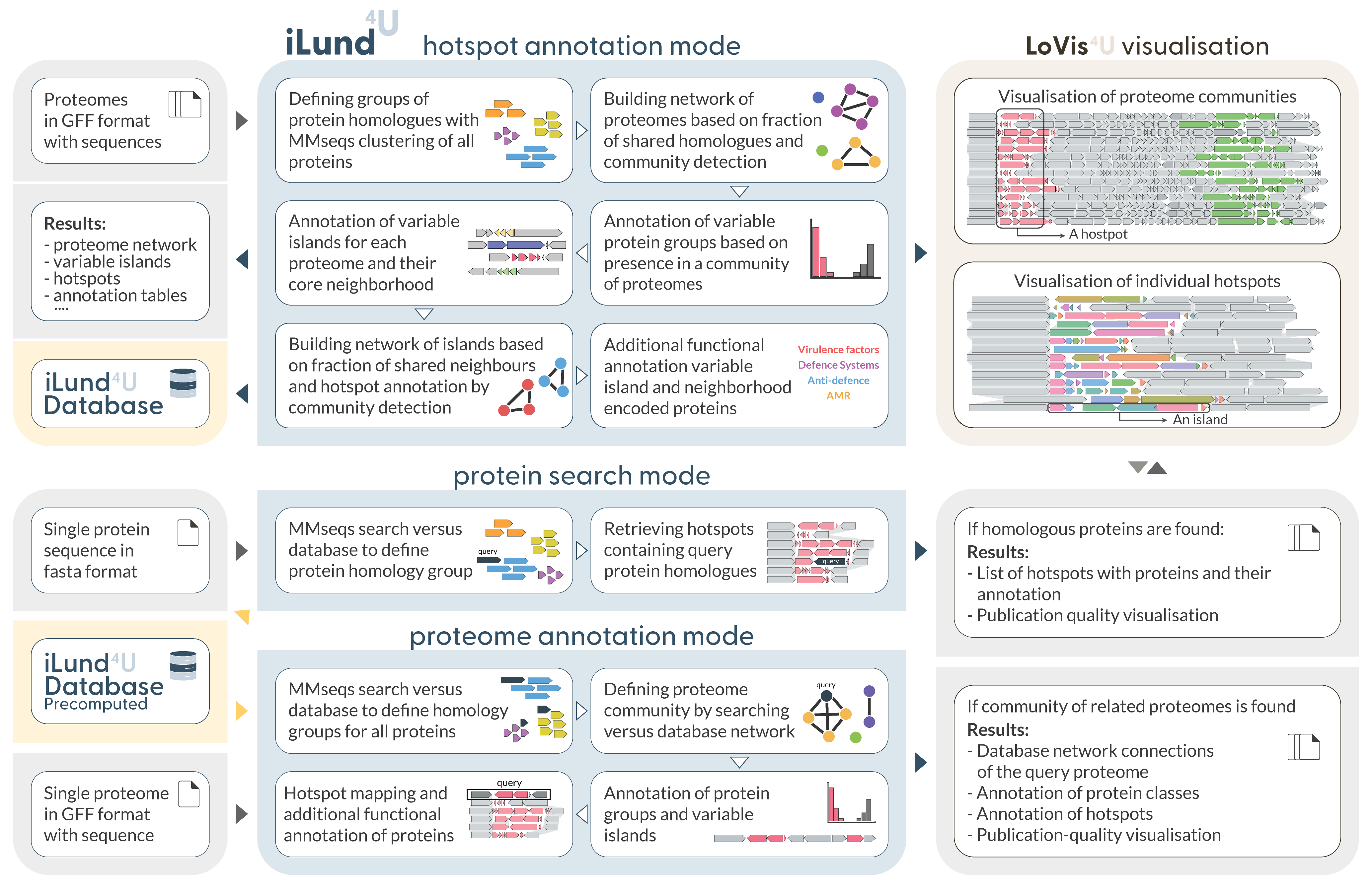
Databases
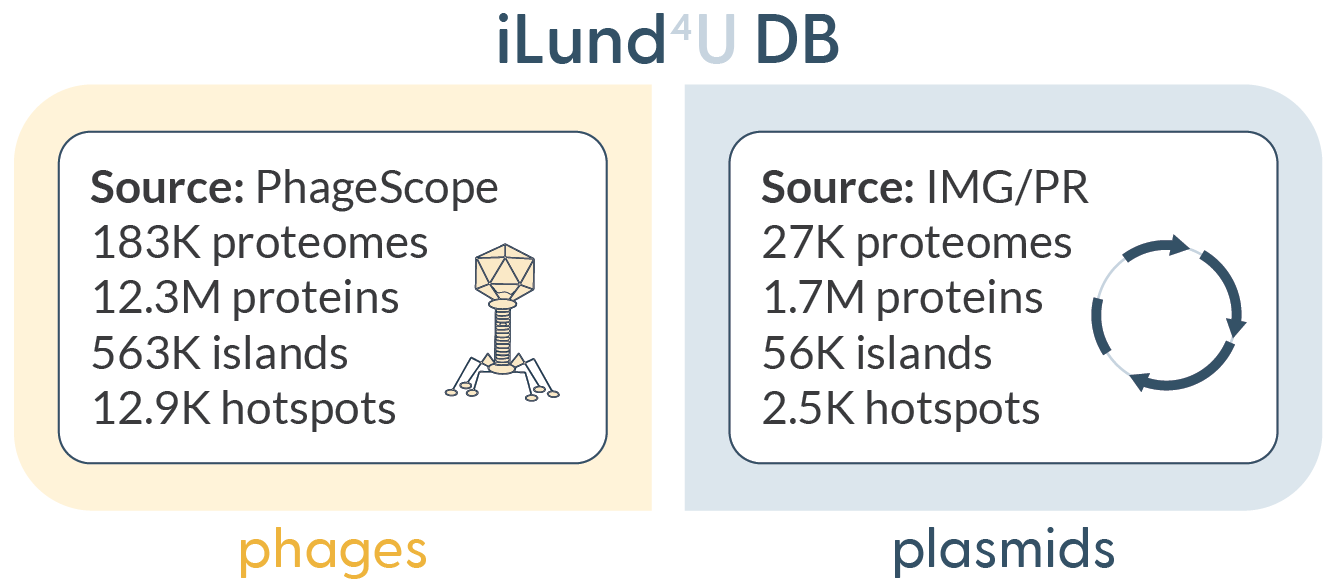
iLund4u has two precomputed databases of hotspots built on phage and plasmid sequences. The database of phage hotspots was built by running hotspot annotation mode on all available PhageScope database sequences (~870K genomes, September 2024). For the plasmid hotspot database we ran hotspot annotation mode on the IMG/PR plasmid database (~700K sequences, June 2024).
Submission form
Reference
If you find iLund4u useful, please cite:
Artyom. A. Egorov, Vasili Hauryliuk, Gemma C. Atkinson, Systematic
annotation of hyper-variability hotspots in phage genomes and plasmids
bioRxiv 22024.10.15.618418; doi:
10.1101/2024.10.15.618418
Authors & Contact
iLund4u is developed by Artyom Egorov at the Atkinson Lab, Department of
Experimental Medical Science, Lund University, Sweden.
We are open for suggestions of how we can extend and improve iLund4u functionality.
Please
don't hesitate to share your ideas or
feature requests.
Please contact us by e-mail or use GitHub Issues to report any technical problems related to iLund4u. You can also use Discussions section for sharing your ideas or feature requests!